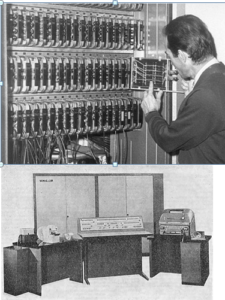
UMC-1
The UMC ( Universal Digital Machine ) computer family was developed at the ELWRO (later Centrum Komputerowych Systemów Automatyki i Pomiarów Mera Elwro) factory in Poland, first in a vacuum tube (UMC-1) and then further developed in a semiconductor (UMC-10) version.
Below we will describe the first one in more detail (picture).
Use
Geodetic calculations
Budapest Geodesy and Cartography Company (BGTV)
Structure
Central unit
Word processing machine: 36 bpW
- controller: on.
- main magazine: replaced by magnetic drum
- calculator: individual fixed-point operations programs; programs for the 4 basic operations, exponentiation and radical extraction
Periphery
- backup storage: magnetic drum 4 sw
- external devices:
- punched tape reader
- telegraph operator, Siemens T-37i
It had no cooling system, so cooling had to be provided externally.
Operation
Fixed point operation speed: 100 ips
The decimal number system used was a -10-based, so-called negadecimal system. Accordingly, the weighting factor of each place value was positive in even-numbered places and negative in odd-numbered places; from right to left, it was 1, -10, 100, -1000, 10000, etc. Thus, the rules of operations became much more complicated.
Its calculator was implemented by programs developed to perform individual operations; these were written by the designer Z. Pawlak for the 4 basic operations, as well as exponentiation and radical extraction. Some operation programs were also designed for the negabinary (base-2; 1, -2, 4, -8, 16, -32 base) number system.
| Negadecimal numbers | Negabinary numbers | |||||||||
| 0,…9 | u.a. | -1 | 19 | 0, 1 | u.a. | -1 | 11 | |||
| -2 | 18 | 2 | 110 | -2 | 10 | |||||
| 10 | 190 | -10 | 10 | 3 | 111 | -3 | 1101 | |||
| 11 | 191 | -11 | 29 | 4 | 100 | -4 | 1100 | |||
| 19 | 199 | -19 | 21 | 6 | 11010 | -6 | 1110 | |||
| 20 | 180 | -20 | 20 | 8 | 11000 | -8 | 1000 | |||
| 99 | 119 | -99 | 1901 | 10 | 11110 | -10 | 1010 | |||
| 100 | 100 | -100 | 1900 | 12 | 11100 | -12 | 110100 | |||
| 123 | 283 | -123 | 1937 | 100 | 11010100 | -100 | 11101100 | |||
Program set
It had no operating system.
There were no programming languages; programming could be done in machine code.
Action execution programs.
Historical curiosities
The first machine was placed at the Institute of Cartography in Warsaw (Institutu Kartografii w Warsowie). For this machine, Anton Kilińskí was posthumously awarded the IEEE Computer Pioneer Award in 1996.
After 1964, ELWRO switched to the production of semiconductor computers; such as the ODRA 1204 computer and later the UMC-10.
The factory was purchased by Siemens in 1993 and soon shut down.
Resources
Description of nega.... type systems: Negative base (English).
https://en.wikipedia. org/wiki/Negative_base
Created: 2024.04.27. 21:56
Last modified: 2025.02.25. 14:36